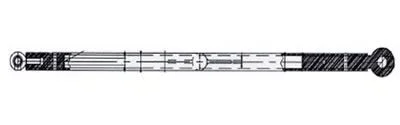
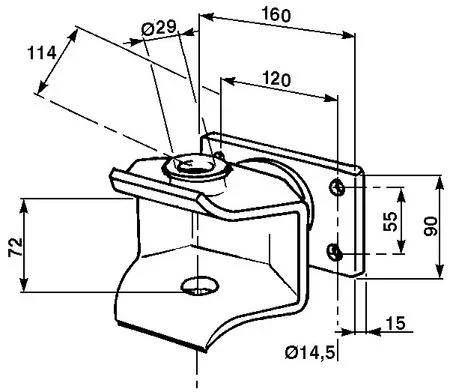
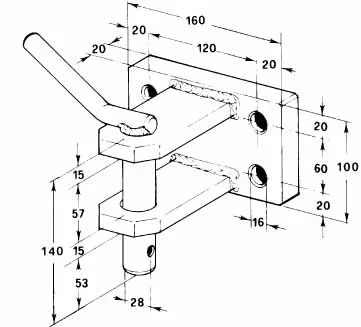
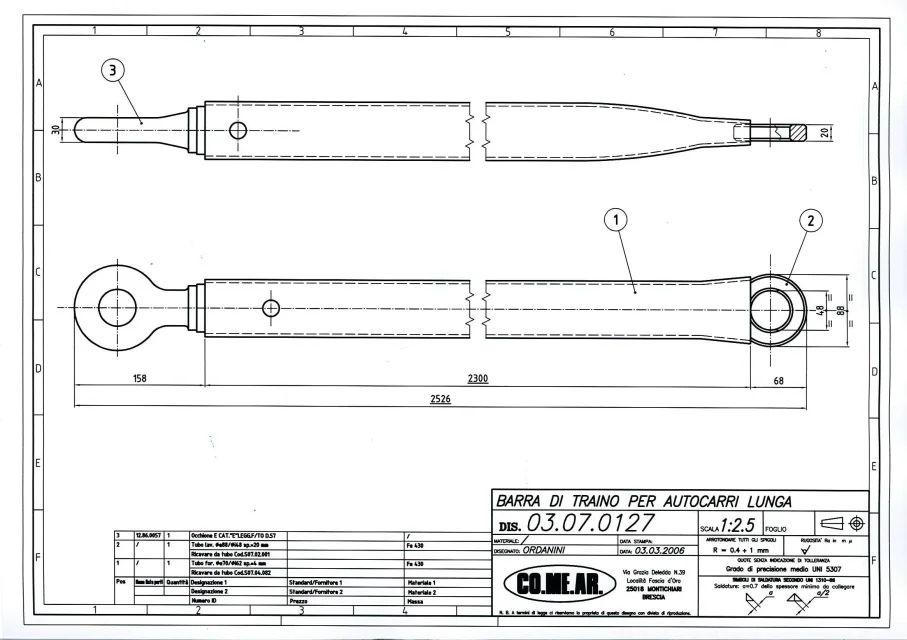
thanks for your precious time, I looked on the net I found this for the regulations:
with regard to structural resistance, the standard dictates the need to define the capacity of the hook according to the horizontal load (d) and the vertical static load (s) supported. the first is expressed according to the technical masses driving and towed (mt and mr respectively) according to the formula below, while the second is directly expressed in “dan
d=g xm x mr/mt + mr
the tests, are conducted, applying a f force that has a horizontal component (fh) a force proportional to d depending on the type of stress (progressive or alternating) and as a vertical component (fv) once and a half the vertical static load
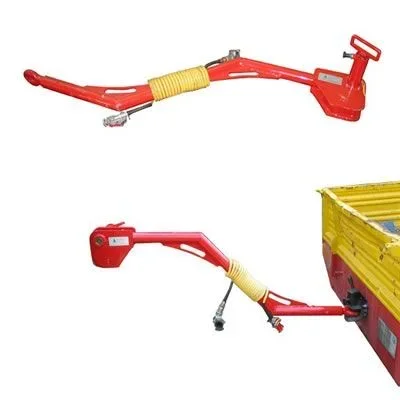
the norm cuna nc 338-02 defines real categories of hooks, referring to applications of typically Italian towing systems. for each of these categories, dimensions and capacity are defined, while on homologation tests are required with static load applications, also recognised at Community level. depending on the product in development, it is possible to perform structural numerical analysis also for such tests obtaining results and information such as those mentioned for fatigue tests
1. the semotive operating machine must be set up with type hook approved according to the tables or approved in accordance with Community rules established for semotive agricultural machinery or for motor vehicles.
2. The hauled operator must be set up with type-approvals approved according to the sewage tables or approved in accordance with Community rules established for agricultural machinery or for trailers.
2.1 In the event of a set-up with a tow-eye corresponding to the cuna nc 438-06 table, it can be driven by semovent machines or by agricultural tractors towed with tow hooks corresponding to the cuna nc 338-02 table.
2.2 in the case of equipment with attack devices in accordance with Directive 94/20/ce or with the tables provided for in Article 438-40 and in Article 438-55, it can be driven by vehicles for the carriage or by machines operating on the road, equipped with attack devices in accordance with Directive 94/20/ce or with the tables provided for in Article 138-55.
art. 3.
towable mass of semovent machines
1. the maximum value of the trailerable mass identified as the difference between the maximum mass at full load of the complex, consisting of the semotive operating machine and the machine operator towed, and the maximum mass at full load of the semotive operating machine: This value is subject to compliance with the tow ratio referred to in Article 1, which cannot exceed the value of:
(a) 1 for rubberized wheel-driven machines, for non-moulded wheel-operating machines or for those with a brake-free machine;
(b) 2 for rubberized-wheel-drive-driven machines, for non-moulded wheel-operating machines or for those clinging machines, whatever the type of braking of the complex;
technical parameters of towing systems
value d: it is defined as the theoretical reference load for the determination of the dynamic horizontal theoretical force that the driving vehicle and the trailer exchange; dc value: it is defined as the theoretical reference load for determining the dynamic horizontal theoretical force that the driving vehicle and the central axis trailer exchange; v value: is defined as the theoretical reference load for the determination of the dynamic vertical theoretical force that the driving vehicle and the central axis trailer with mass greater than 3.5 ton exchange; s value: it is the static vertical load that the central axis trailer transmits to the hook in static conditions; u value: it is the vertical load transmitted from the semi-trailer to the saddle.
- towing hooks and eyelets 1.1 - traditional trailers
in this case the characteristic technical parameter is as follows:
d = g xt x r/t + r
where: g = acceleration of gravity taking 9.81 m/s2; t= represents the maximum technically admissible mass, expressed in ton of the driving vehicle; r= represents the maximum technically admissible mass of the trailer expressed in ton.
c) 3 for rubberized wheel operating machines, if the mechanical type brake device;
d) 4 for rubberized wheel machines, if the braking device of the mixed and automatic type complex;
(c) 5 for rubberized wheel machines, if the braking device of the continuous and automatic type complex.