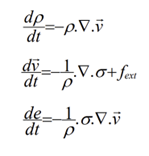Friction-Stir Welding Using LS-DYNA Smooth Particle Hydrodynamics (SPH)
Friction Stir Welding (FSW)
- Friction stir welding (FSW) is a solid-state joining process that creates high-quality welds in metals, primarily aluminum and its alloys. It involves a rotating tool that plunges into the joint between two workpieces.
- The tool generates heat and softens the material without melting it. As the tool rotates, it stirs and mixes the softened material, forming a solid-state bond.
- FSW has advantages such as minimal distortion, and the ability to join dissimilar materials.
- It is used in the aerospace and automotive industries to manufacture strong and reliable components.
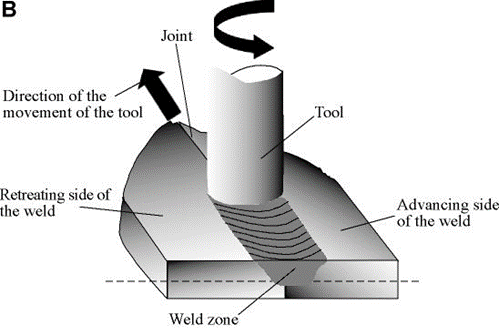
Figure 1: Friction Welding Process
LS-DYNA Smooth Particle Hydrodynamics (SPH)
- The SPH method is a Lagrangian mesh-free numerical technique that can be used to simulate different physics from fluid dynamics problems as well as for structural problems that contain high speed and large deformation.
- This method discretizes the continuum domain into particles, where each particle carries certain properties like mass, velocity, and other relevant variables.
- Like FEM Method, the SPH method solves conservation equations to solve for velocity, pressure and energy.
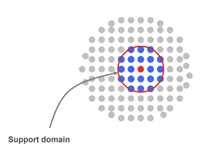
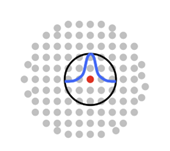
- These particles interact with each other based on the smoothing function (SPH kernel function), which determines the rate of change of influence neighbouring particles each other.
|
Conservation Equations |
Support Domain 2D Representation |
Kernel function 2D Representation |
- Below are animations illustrating friction stir welding simulation utilizing Smooth Particle Hydrodynamics:
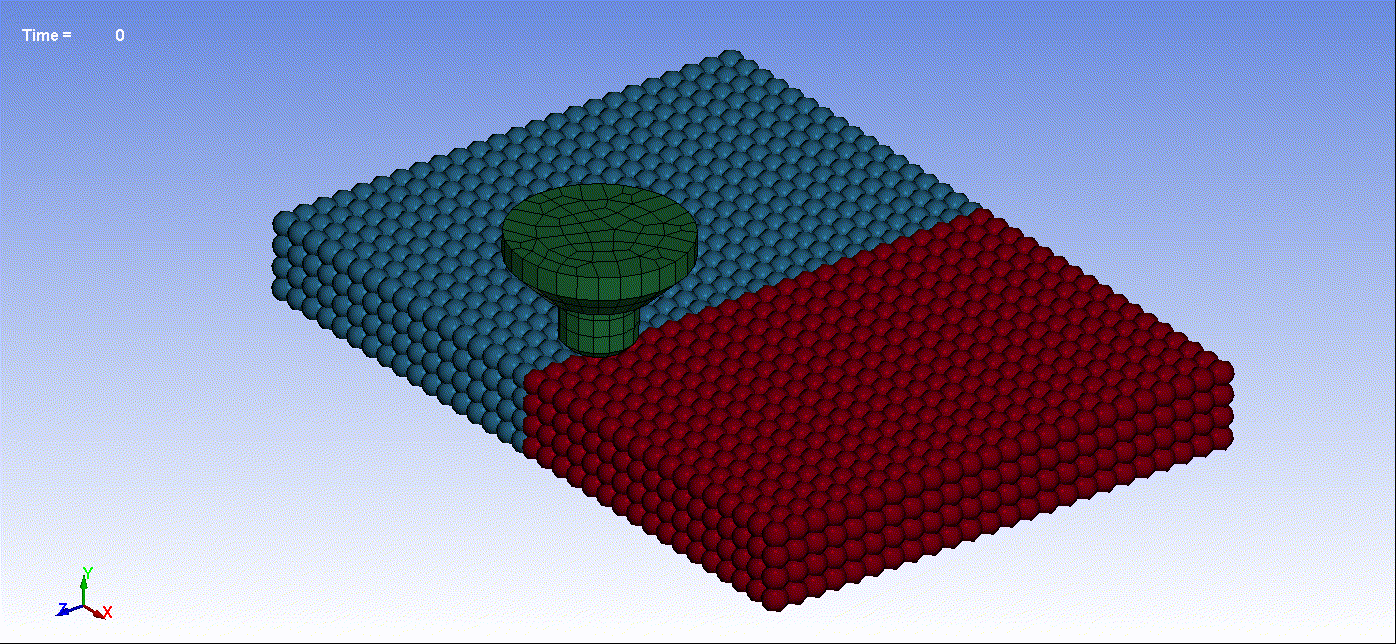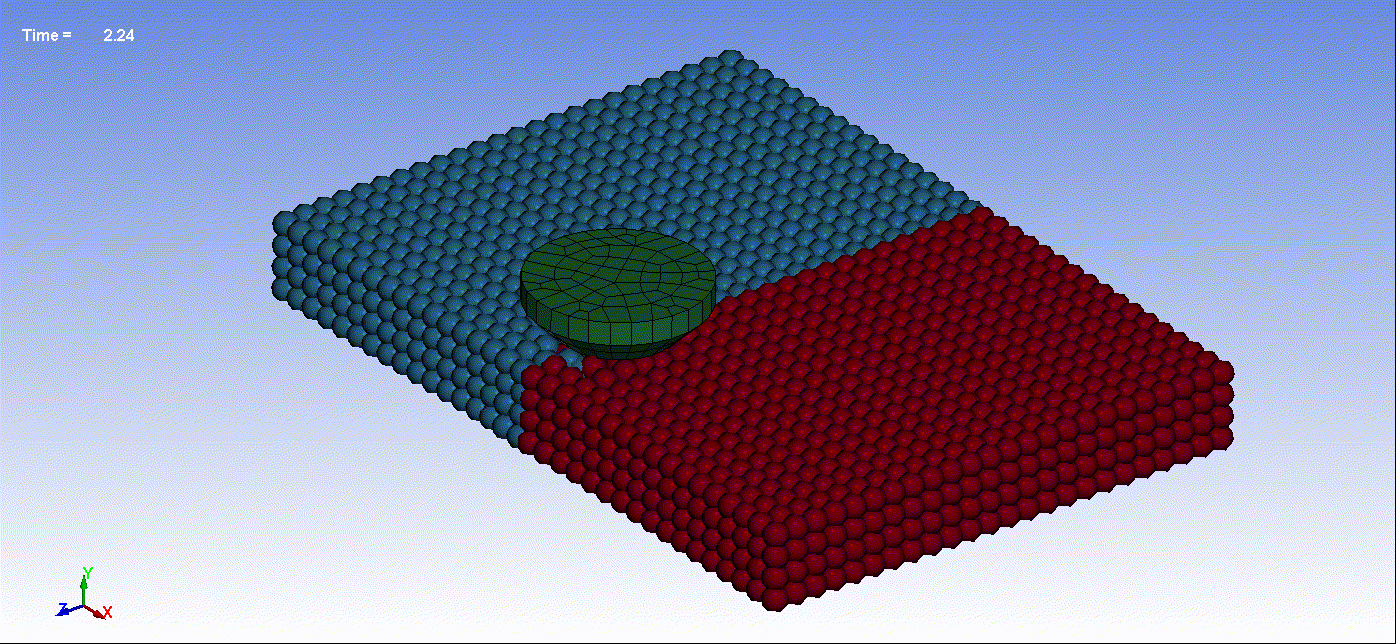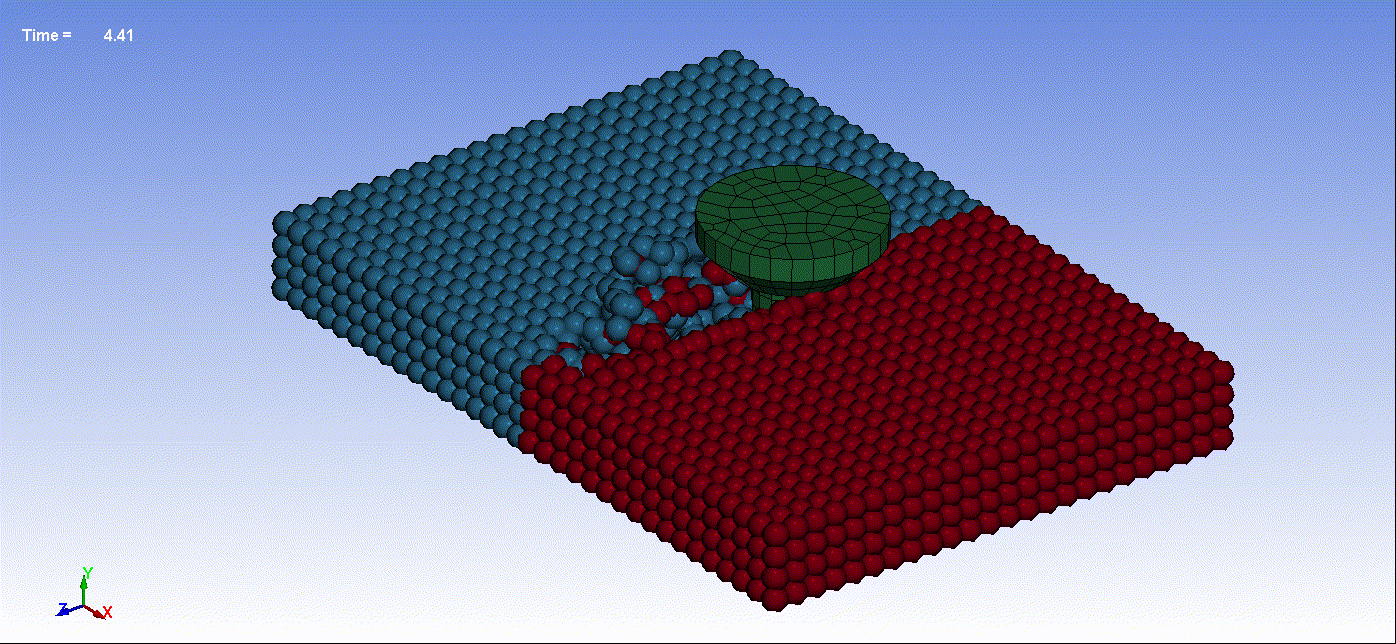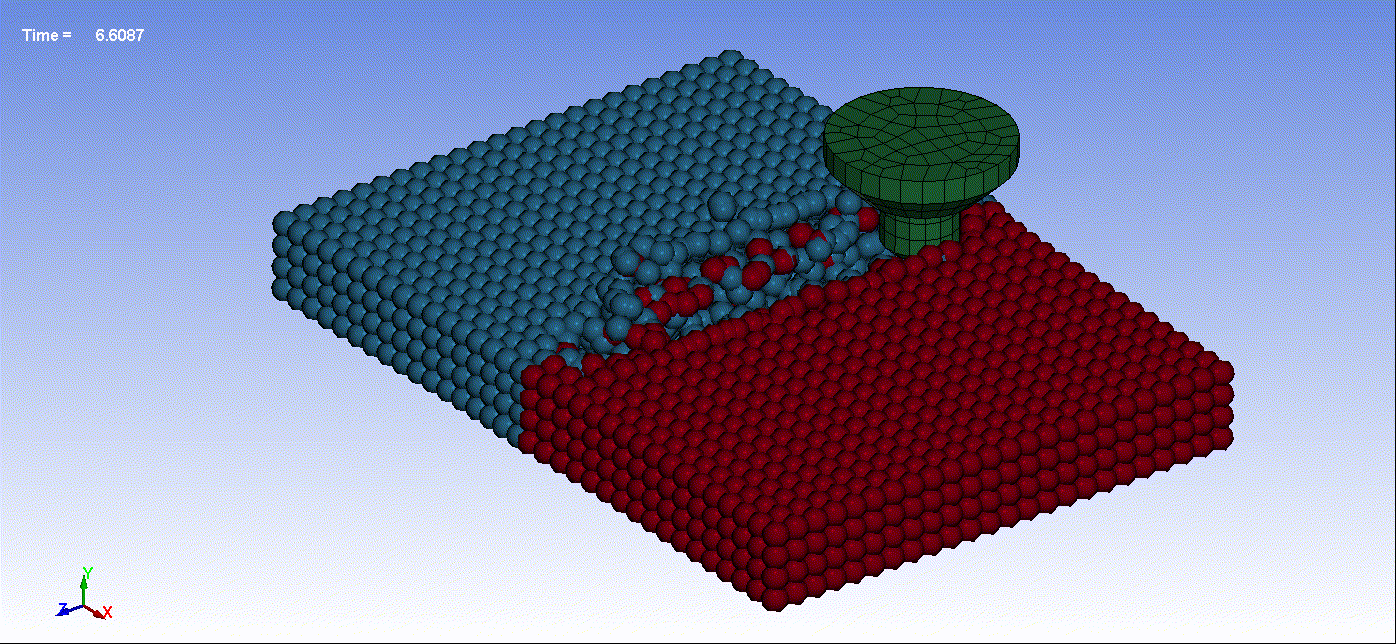
Animation 1: Friction Stir Welding Result
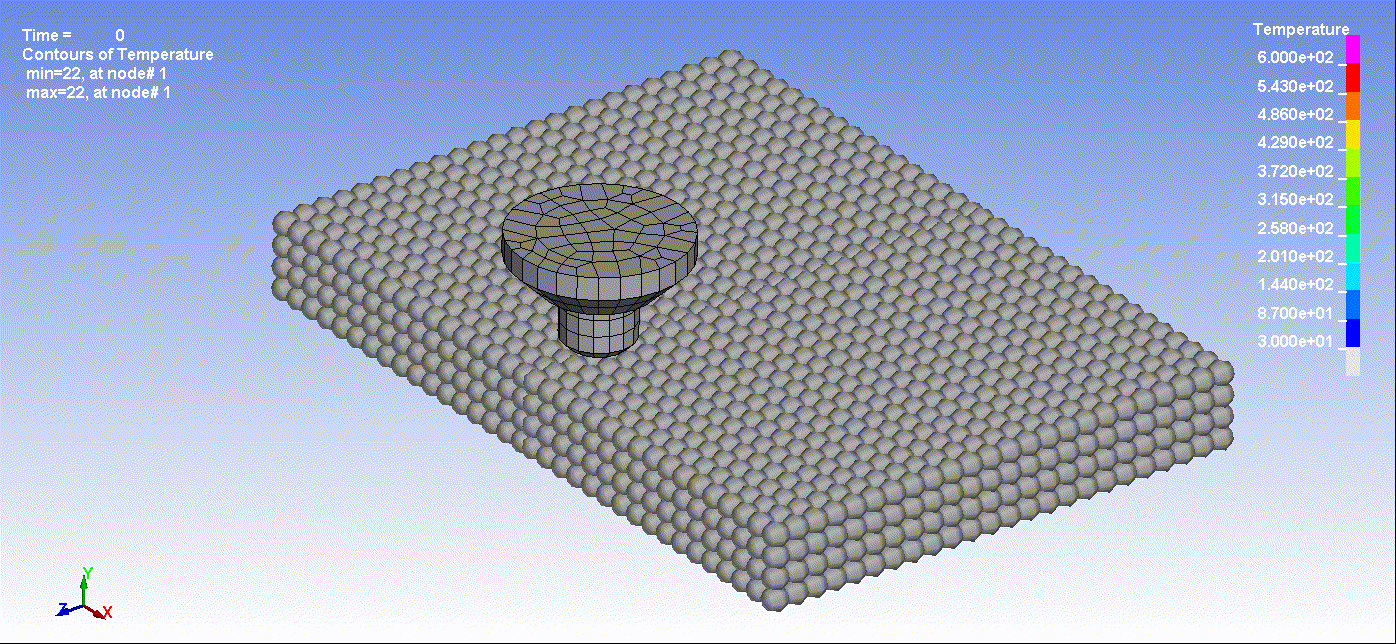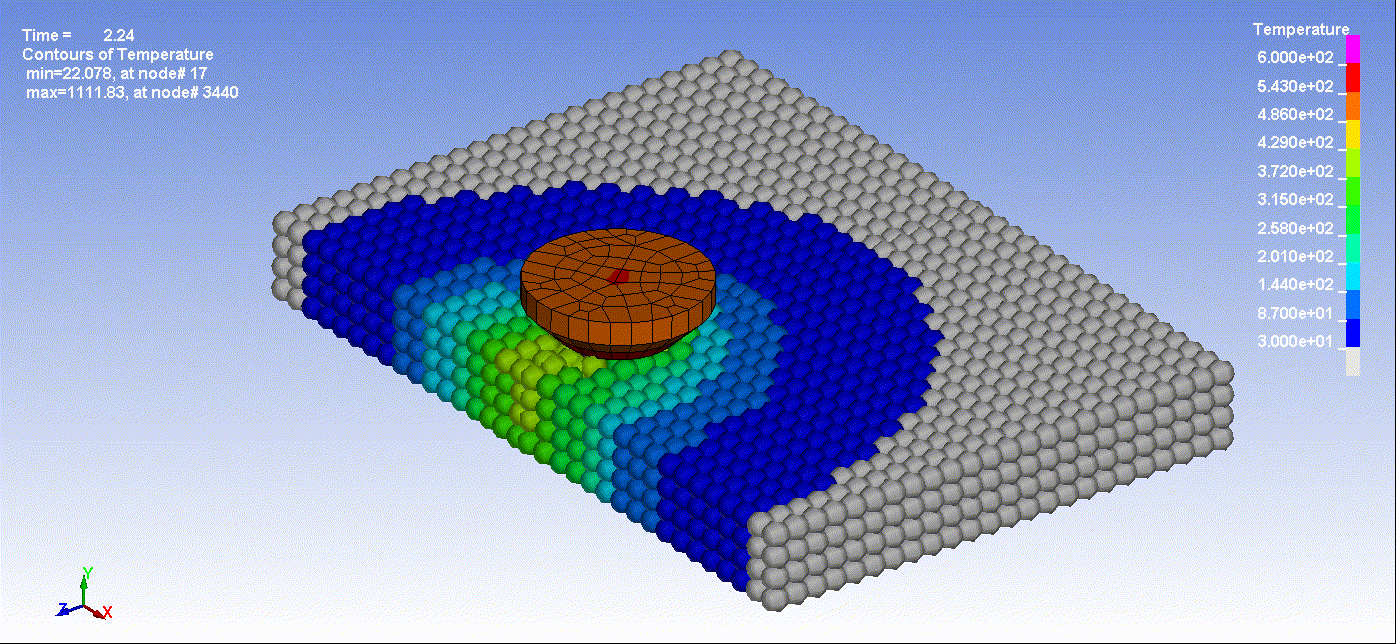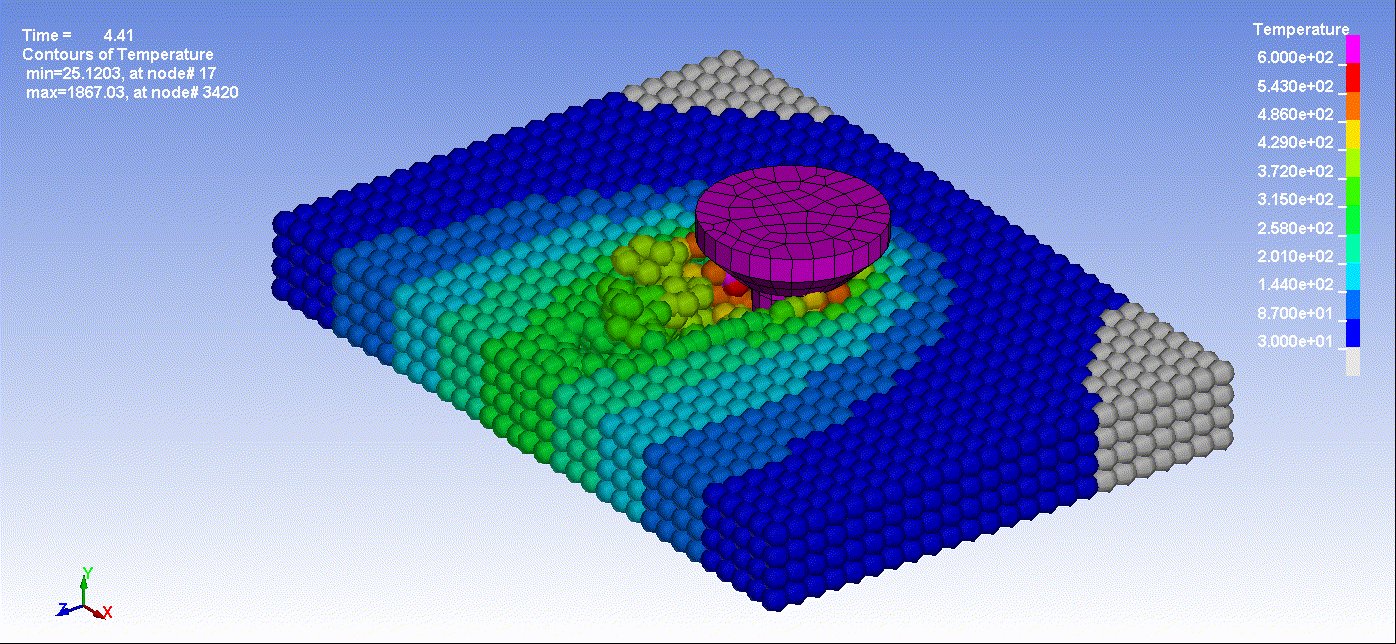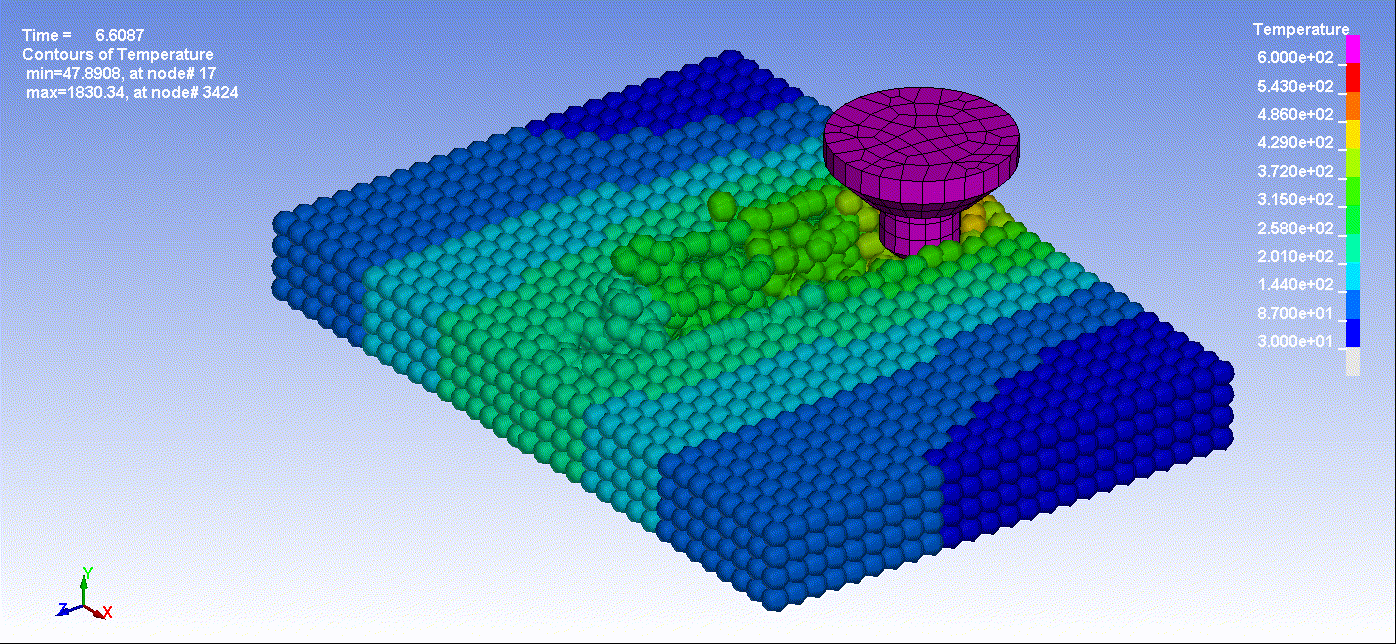
Animation 2: Friction Stir Welding Temperature Result By Time