Join the forum for Designers!
Your expertise is vital to the community. Join us and contribute your knowledge!
Join the Forum NowShare, learn and grow with the best professionals in the industry.
Some industries (like automotive and aerospace) have used 3D printing for decades. With the introduction of new AI software, advanced machines, and materials, many sectors within the healthcare industry are gaining momentum due to these innovations. Biocompatible implants, surgical guides, and 3D printed models for pre-surgical practice are only a few examples of the driving forces behind the rapid growth of the medical 3D printing industry.

Medical Digital Workflow Starts with Segmentation
Medical image segmentation is the initial workflow process that includes isolating DICOM medical images, such as CT scans or MRI scans, into distinct structures or regions of interest (ROI). The goal for segmenting this type of data is to identify and explore areas of the anatomy, whether it’s tissue, cardiovascular, or bone. For example, virtually positioning CAD implants or creating water-tight mesh files for 3D printing patient-specific anatomical models.
Segmenting medical images can be quite complex and time-consuming, but advances in AI software are making this process easier. Companies like AXIAL3D have recognized this step in the workflow and are providing services to many medical clinics and research institutes nationwide.
DICOM to Print
DICOM (Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine) images are not exported to STL data immediately. After the primary segmentation process, the files go through a secondary process for noise spike removal, surface smoothing, and filling any holes to ensure the model has a clean, water-tight surface ready for 3D printing.
Stratasys has developed an entire Healthcare team focused on delivering high-quality 3D printed anatomical models. Their portfolio includes the J850 Digital Anatomy and J55 Medijet PolyJet 3D printers, known for their unmatched accuracy, realism, and repeatability.

These printers use a variety of bone and tissue matrix materials, along with full-color Vero materials, which help surgeons trust this new method of interacting with patient data.
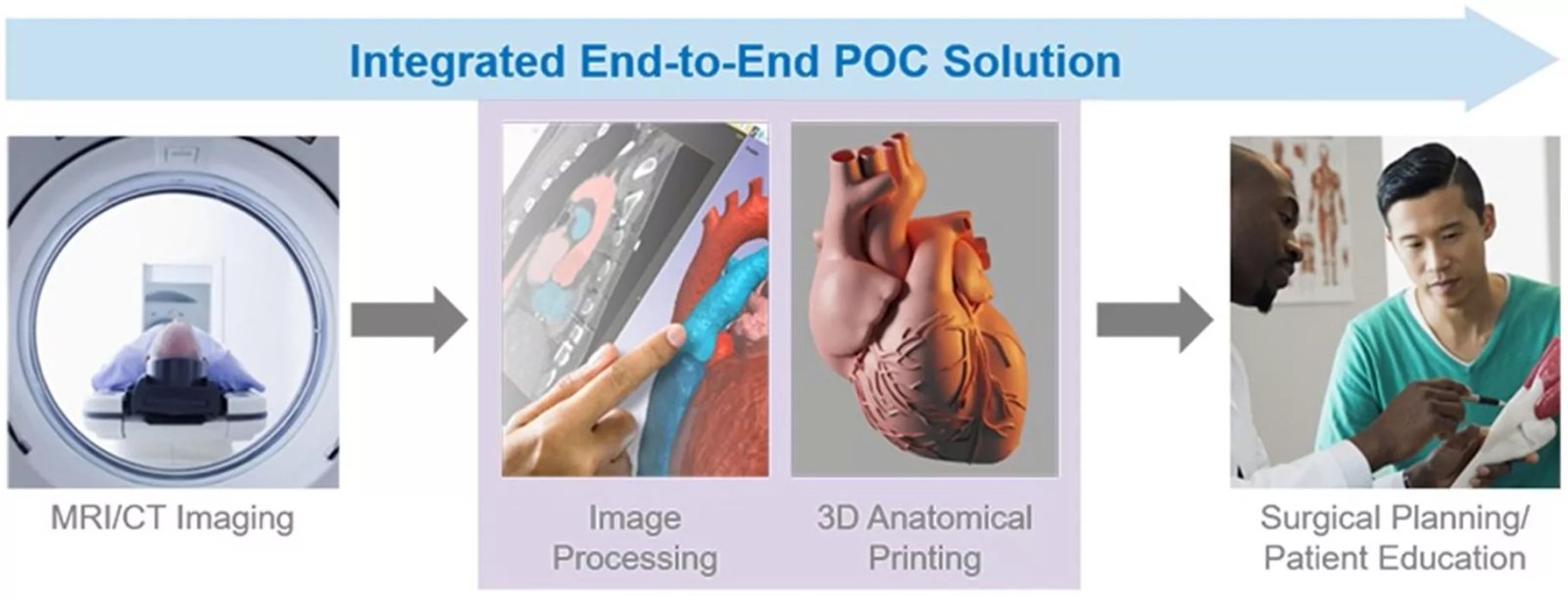
Benefits of an End-to-End Digital Solution
Holding an accurate replica of a patient’s anatomy provides more understanding of the surgery site and process. Moreover, it enables the creation of prostheses and custom implants. This point-of-care (POC) solution has significantly reduced surgical times and improved recovery, leading to higher patient satisfaction.
Many DICOM to Print (D2P) companies hold 510(K) clearance, which allows surgeons and lab technicians to use this validated workflow in operating rooms and surgical centers. Clinicians like to use 3D prints of medical imagery as a physical reference before surgery, which allows effective visualization and surgical planning. While there are still many obstacles facing quality control regulations and standardization of the workflow processes, many companies are striving to meet these strict guidelines to advance the use of this End-to-End D2P workflow.
Join the forum for Designers!
Your expertise is vital to the community. Join us and contribute your knowledge!
Join the Forum NowShare, learn and grow with the best professionals in the industry.

